Trigeminal neuralgia is more than just facial pain—it's a condition that can affect every part of a person’s life. The intense, sudden jolts of pain it causes can be physically and emotionally debilitating. Many people suffer in silence, misdiagnosed or misunderstood. That's why spreading awareness and knowledge about this condition is so important.
If you're wondering, what is trigeminal neuralgia? everything you need to know is right here in this article. We'll cover its definition, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and how to live with it.
What Is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
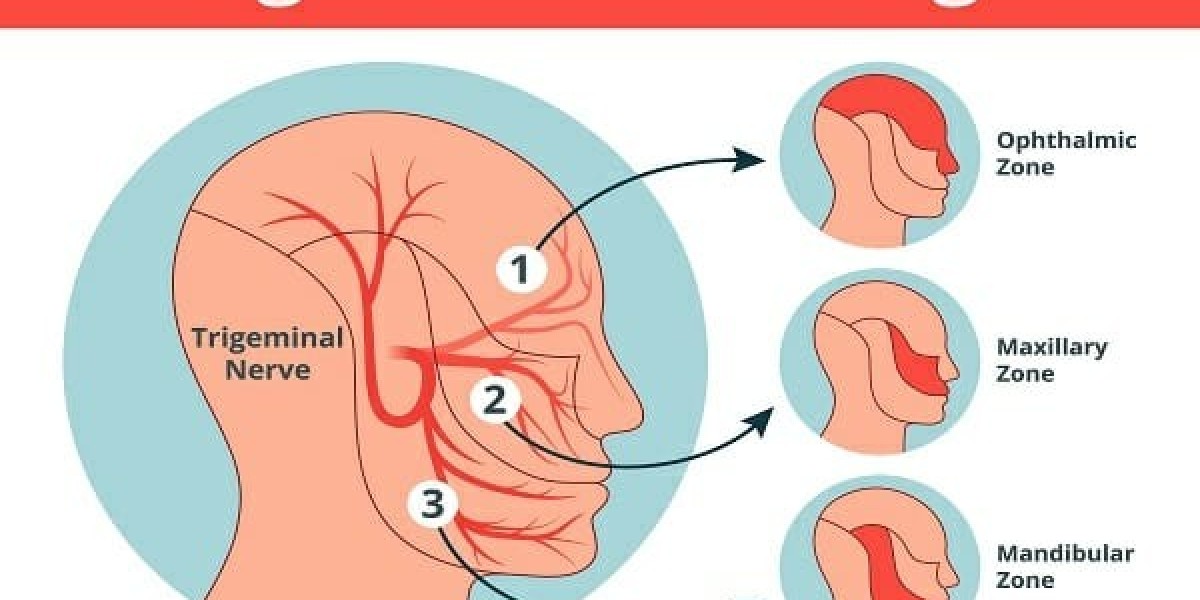
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a chronic pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sending sensations from your face to your brain. When someone has TN, even mild stimulation of the face—such as brushing your teeth or feeling a breeze—can trigger a painful reaction.
The condition is often described as one of the most painful known to medicine. Some people compare it to an electric shock, stabbing pain, or sudden burning in the face.
It’s more common in people over the age of 50 and is slightly more prevalent in women.
Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Understanding the root causes can help in choosing the best treatment strategy. TN can be divided into two types: primary and secondary.
Primary TN
Primary TN is most often caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve by a blood vessel. This pressure damages the protective covering of the nerve (myelin sheath), causing the nerve to misfire and send intense pain signals to the brain.
Secondary TN
Secondary TN can result from:
Multiple sclerosis (MS), which damages the myelin sheath
Tumors pressing against the trigeminal nerve
Facial injuries or trauma
Brain lesions
In some rare cases, no clear cause is identified.
Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms can vary, but the following are common:
Sudden, intense, and shooting pain in the face
Pain episodes lasting from a few seconds to two minutes
Pain triggered by touch, movement, or even wind
Periods of frequent attacks followed by remission
Pain usually on one side of the face
Pain that affects the jaw, cheek, teeth, lips, or gums
Between attacks, some people may experience a dull ache or burning sensation.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
TN is diagnosed mainly based on your medical history and symptoms. A neurologist may perform:
Neurological exams to test facial sensitivity
MRI scans to detect nerve compression or rule out conditions like MS or tumors
Blood tests in rare cases to exclude infections or inflammation
Correct diagnosis is crucial since facial pain can stem from various causes like dental issues or migraines.
Treatment Options for Trigeminal Neuralgia
If you're asking what is trigeminal neuralgia? everything you need to know includes learning how it’s treated. Thankfully, TN can be managed effectively through various medical and lifestyle approaches.
1. Medications
Anticonvulsants
Carbamazepine is usually the first-line medication for TN. Others include oxcarbazepine, gabapentin, and lamotrigine. These drugs help calm overactive nerves.
Muscle Relaxants
Drugs like baclofen can be used alone or in combination with anticonvulsants to control spasms and pain.
Tricyclic Antidepressants
These may help manage pain in cases where nerve pain has a burning or aching quality.
2. Surgery
If medications stop working or cause side effects, surgical interventions may be recommended.
Microvascular Decompression (MVD)
A surgeon moves or removes the blood vessel that’s pressing on the nerve. This is the most effective long-term treatment in many cases.
Rhizotomy
This involves damaging the nerve fibers to block pain signals using heat, glycerol, or balloon compression.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
A non-invasive procedure where focused radiation is used to reduce the pain signals from the nerve.
Complementary and Lifestyle Approaches
Treatments work best when combined with self-care and lifestyle changes. Here are some helpful strategies:
1. Avoid Triggers
Track and avoid known triggers like chewing, cold wind, or brushing your teeth
2. Practice Stress Relief
Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help calm the nervous system
3. Diet & Nutrition
Ensure a diet rich in Vitamin B12, magnesium, and anti-inflammatory foods
4. Join Support Groups
You’re not alone. Online and offline communities can offer advice and encouragement
5. Stay Informed
The more you know about your condition, the better you can manage it. Sites like FlowCare offer trusted information and resources.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with TN can lead to anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. Pain unpredictability adds emotional stress. Here’s how to manage the mental aspect:
Seek counseling or therapy
Talk openly with friends and family
Join a chronic pain support group
Practice daily gratitude or journaling
Addressing mental health is a crucial part of treatment.
Daily Life with TN: Tips for Coping
Use a scarf to shield your face from wind
Avoid overly hot or cold drinks
Use soft toothbrushes and mild toothpaste
Plan your meals and conversations around your pain schedule
Communicate with your employer about your condition
Conclusion
Trigeminal neuralgia may be rare, but it’s real and life-altering. The good news is that it's manageable. Early diagnosis, a combination of treatments, and a solid support system can drastically improve the quality of life. If you ever asked yourself, what is trigeminal neuralgia? everything you need to know—we hope this article gave you the clarity and direction you need.
Visit FlowCare’s TN Support Page for more help, advice, and community support.
FAQs
1. Is trigeminal neuralgia dangerous?
While not life-threatening, TN can significantly affect daily life. It can lead to severe emotional distress if left untreated.
2. What triggers a TN episode?
Triggers vary, but common ones include touch, wind, eating, brushing teeth, or even smiling.
3. Can TN go away on its own?
Some patients experience remission periods, but most require medical management.
4. What specialist treats trigeminal neuralgia?
A neurologist or neurosurgeon usually manages TN, especially in severe or treatment-resistant cases.
5. Are there natural remedies for TN?
While not cures, stress management, acupuncture, and dietary changes may help reduce symptoms.