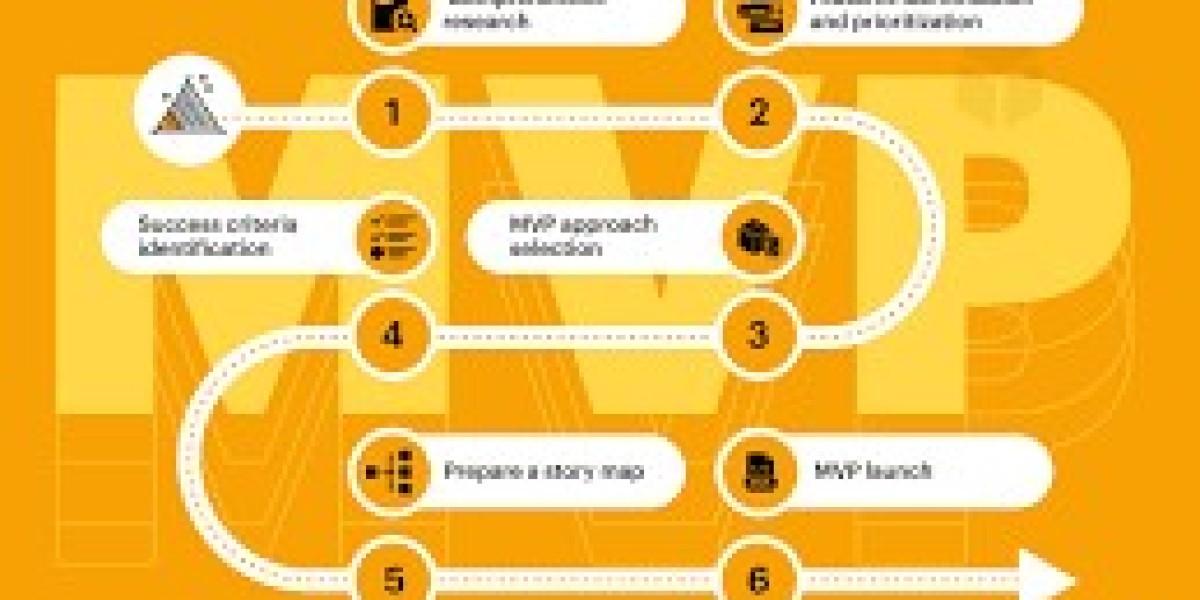
A Minimum Viable Product, often abbreviated as MVP, represents the most distilled version of a healthcare application—engineered with just enough functionality to validate its viability. In the digital health ecosystem, this concept acquires amplified significance. Applications intersect with human well-being, clinical accuracy, and regulatory oversight. Therefore, an MVP is not merely “minimal”; it is precision-focused, compliance-aware, and outcome-driven. A Healthcare App Development Company approaches MVP creation as a strategic calibration exercise. The objective is to sculpt a functional prototype that demonstrates clinical value while conserving capital and development velocity.
Why MVPs Are Critical for Healthcare Startups
Healthcare innovation is capital intensive and risk laden. MVPs mitigate both variables. By launching a controlled, feature-focused product, startups can validate hypotheses, attract investors, and refine operational models. Early adoption metrics illuminate what resonates with users and what requires recalibration. This iterative validation prevents large-scale financial miscalculations and accelerates product-market alignment.
2. Market Research and Ideation Strategy
Identifying Healthcare Gaps and User Pain Points
Every impactful healthcare solution originates from a tangible problem. Market research involves ethnographic analysis, stakeholder interviews, and workflow observation. Friction points—delayed diagnostics, fragmented records, inaccessible specialists—become innovation catalysts.
A Healthcare App Development Company synthesizes these insights into actionable product concepts, ensuring the MVP addresses genuine clinical and operational deficiencies rather than hypothetical conveniences.
Competitor Analysis and Trend Mapping
The digital health marketplace is densely populated yet unevenly optimized. Competitor analysis dissects existing applications—their features, limitations, monetization models, and user sentiment. Simultaneously, trend mapping evaluates emergent currents such as remote monitoring, AI triage, and decentralized health data.
This dual analysis informs differentiation strategy. The MVP is positioned not as a replica but as an evolutionary advancement.
3. Regulatory Planning and Compliance Readiness
Understanding Healthcare Regulations (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)
Compliance is the spinal column of healthcare technology. Regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, and regional health data laws dictate how patient information is stored, transmitted, and accessed. Noncompliance carries severe financial and reputational repercussions.
A Healthcare App Development Company embeds compliance protocols from inception—encrypting data pipelines, anonymizing patient identifiers, and implementing audit trails that withstand regulatory scrutiny.
Risk Mitigation and Legal Framework Alignment
Risk in healthcare applications extends beyond data breaches. Clinical misinterpretation, device integration errors, and workflow disruptions all pose liabilities. Legal alignment involves structured documentation, consent frameworks, and disclaimers integrated seamlessly into the user journey.
Proactive risk mitigation fortifies the MVP against litigation while reinforcing institutional trust.
4. Feature Prioritization and Product Scope
Core vs. Advanced Feature Segmentation
Feature sprawl is the nemesis of MVP efficiency. Prioritization frameworks—such as MoSCoW or value-effort matrices—segregate essential functionalities from aspirational enhancements. Core features may include appointment scheduling, secure messaging, or health record access. Advanced modules—AI diagnostics or wearable integrations—are deferred.
This disciplined minimalism accelerates deployment without diluting clinical utility.
Patient-Centric Functionality Planning
Healthcare applications serve diverse stakeholders, yet patients remain the gravitational center. MVP features are sculpted around patient convenience, clarity, and empowerment. Medication reminders, symptom trackers, and teleconsultation portals enhance engagement while improving adherence to treatment regimens.
5. UI/UX Architecture for Healthcare MVPs
Designing for Accessibility and Usability
Healthcare users span age groups, literacy levels, and physical abilities. Interface design must therefore privilege clarity over ornamentation. Large typography, intuitive iconography, and voice navigation features ensure usability across demographics.
A Healthcare App Development Company employs human-centered design methodologies, validating interfaces through usability testing and behavioral analytics.
Workflow-Centric Interface Structuring
Clinical efficiency depends on workflow harmony. Interfaces are structured to mirror real medical processes—triage, consultation, documentation, follow-up. When digital pathways align with practitioner routines, adoption resistance diminishes and productivity flourishes.
6. Technology Stack Selection and Integration
Backend Infrastructure and Cloud Frameworks
Scalability begins at the infrastructural level. Cloud-native architectures enable elastic storage, rapid deployment, and secure data redundancy. Microservices frameworks allow modular expansion without systemic disruption.
Such infrastructural foresight ensures the MVP can evolve seamlessly into a full-scale platform.
API Integrations with Healthcare Systems
Healthcare applications rarely operate in isolation. Integration with EHR systems, pharmacy databases, and diagnostic laboratories enhances functional depth. Secure APIs act as connective tissue, enabling synchronized data exchange while preserving confidentiality.
7. Development, Testing, and Iteration Cycles
Agile Development Methodologies
Agile frameworks introduce rhythmic development cycles—sprints, stand-ups, retrospectives. This cadence fosters adaptability. Features are developed incrementally, tested continuously, and refined iteratively.
A Healthcare App Development Company leverages agile methodologies to accommodate regulatory adjustments, stakeholder feedback, and technological refinements without derailing timelines.
Security Testing and Performance Validation
Healthcare MVPs undergo rigorous validation. Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and load simulations ensure resilience under operational stress. Performance optimization minimizes latency—an essential factor when clinical decisions hinge on real-time data access.
8. MVP Launch and Post-Deployment Optimization
Beta Releases and User Feedback Loops
Launch is not the culmination; it is the commencement. Controlled beta releases invite targeted user groups—clinicians, administrators, patients—to interact with the MVP. Their feedback reveals experiential blind spots and functional inefficiencies.
Iterative refinements, guided by analytics and user sentiment, transform the MVP into a mature, market-ready solution.
Scaling the Product Beyond MVP
Once validated, the product enters expansion orbit. Advanced analytics, AI modules, wearable integrations, and multilingual capabilities are layered systematically. Infrastructure scales. Security frameworks deepen. User bases broaden.
Through this evolutionary trajectory, a Healthcare App Development Company converts a modest MVP into a comprehensive digital health ecosystem—capable of redefining care delivery, operational intelligence, and patient empowerment.