For those who have seen these machines in action but have not yet ventured into the world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control), this guide will help demystify their operation and provide a solid foundation for beginners. We will explore what CNC machines are, how they work, and the essential steps involved in using them.
What Is a CNC Machine?
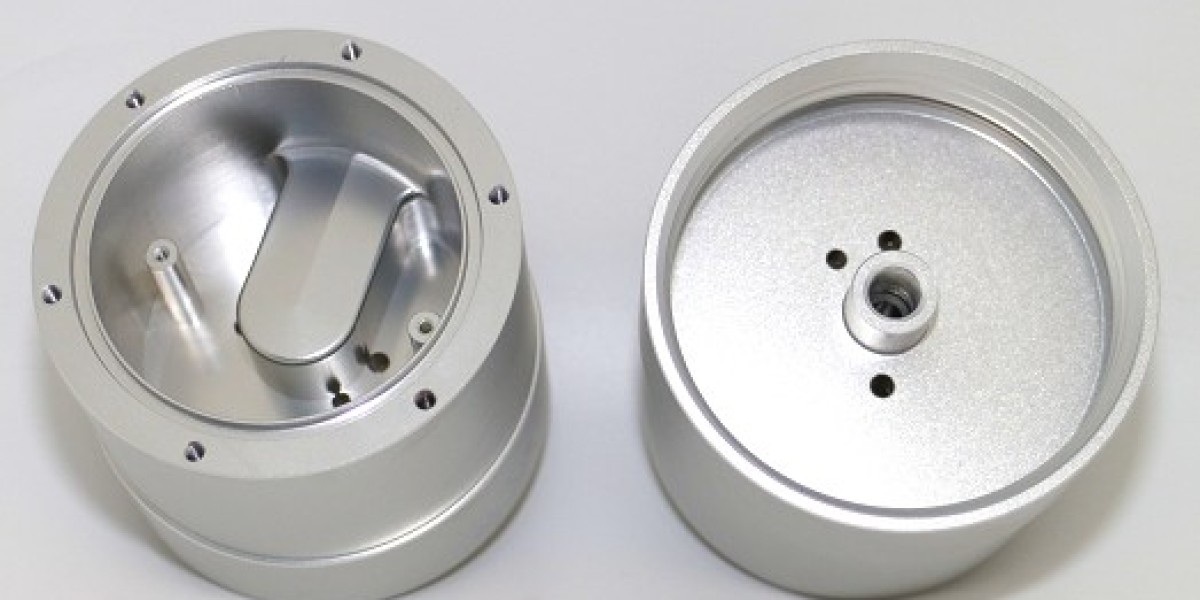
At its core, a CNC machine is a device that uses computer technology to control its movements and operations. The term "CNC" refers to Computer Numerical Control, which means that the machine is programmed via a computer to perform specific tasks. Various types of CNC machines exist, including CNC mills, CNC routers, CNC plasma tables, and even 3D printers.
For our discussion, we will primarily focus on CNC mills and routers. CNC routers are typically designed for cutting softer materials like wood, while CNC mills are more robust and capable of machining harder materials like metal. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for anyone looking to start using CNC technology.
The Anatomy of a CNC Machine
Understanding the basic components of a CNC machine is essential for mastering its use. Regardless of the type, all CNC machines have a few common parts:
Bed: This is the surface on which the material is placed. The bed provides stability and support during the machining process.
Cutting Head (Spindle): This is the part that moves to perform the cutting. The spindle can be a dedicated motor or a standard router attached to the frame.
Tooling: The actual cutting tools used are known as end mills. These tools come in various shapes and sizes, allowing for different types of cuts and finishes.
CNC machines can operate on three axes—X, Y, and Z—allowing for intricate designs and detailed work. More advanced machines may offer additional axes, but for beginners, focusing on the three-axis operation is a good starting point.
The CNC Process: From Design to Production
Using a CNC machine involves several steps, each crucial for ensuring a successful outcome. Below are the primary phases of the CNC process:
1. Design and Toolpath Creation
The first step is to create a design for what you want to cut. Unlike 3D printing, where you can simply download a file and hit "print," CNC machining requires more preparation. Most users design their projects using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This software allows you to create detailed models that will later be converted into toolpaths.
After creating a design, the next phase is to generate toolpaths using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. This software translates the design into specific movements for the cutting head, dictating not just the path but also parameters such as feed rates and spindle speed.
2. Work Holding and Material Setup
Once the design and toolpaths are ready, the next step involves securing the material onto the machine. Proper work holding is crucial because the material will experience various forces during cutting. Using clamps or specialized fixtures, you must ensure that the material is held firmly in place.
For beginners, it’s advisable to familiarize yourself with various work-holding techniques, as improper setup can lead to inaccurate cuts or even damage to the machine.
3. Offsets and Machine Setup
Before initiating the cutting process, it’s essential to inform the machine where the material is positioned. This is done through a process called setting offsets. The machine needs to know the exact location of the material to ensure accurate cuts. This step often involves homing the machine and touching off the tool to establish a reference point.
4. Cutting and Cleanup
Now comes the exciting part: executing the cut. Once you hit "go," the machine will follow the programmed toolpaths to cut the material. It’s important to monitor the process to ensure everything runs smoothly.
After cutting, cleanup is necessary. This often involves sanding or deburring the edges to achieve a polished finish. Depending on the material, additional steps may be required to achieve the desired look.
Choosing the Right CNC Machine
When considering the purchase of a CNC machine, it's vital to ask yourself a few questions to narrow down your options. What materials do you plan to work with? If you intend to primarily cut wood, a CNC router would be suitable. For metals, a CNC mill would be a better fit.
Understanding the scope of your projects and your budget will guide you toward the right choice. For those looking for reliable CNC machining in China, consider exploring options available at CNCLATHING.COM, which offers a variety of CNC services tailored to different needs.
CNC machines can seem intimidating at first, but with a basic understanding of their operation and purpose, even beginners can dive into this fascinating field. By grasping the fundamental concepts outlined in this guide, you can begin your journey into CNC machining with confidence. Whether you aim to create intricate wood designs or precise metal parts, the world of CNC is full of possibilities waiting for you to explore. Embrace the journey, and who knows? You might just find your passion in the precision and creativity that CNC machining offers.
For more information and resources, be sure to check out CNC machining China company to see how you can take your projects to the next level.