Air filtration is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy indoor environment, especially in areas where air quality can be compromised by pollutants, allergens, or chemicals. While traditional air filters have been the go-to solution for most environments, https://www.ast-filter.com/Chemical-Filters are increasingly being used in applications where specific contaminants, such as gases, vapors, or chemical fumes, need to be controlled.
This article will explore the differences between chemical air filters and traditional air filters, their respective uses, benefits, and limitations, and help you determine which type is best suited for your specific air filtration needs.
What Are Traditional Air Filters?
Traditional air filters are designed to remove particulate matter from the air. These particles can range from dust, pollen, and mold spores to pet dander, smoke, and other airborne allergens. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are among the most well-known traditional air filters, renowned for their ability to trap particles as small as 0.3 microns with a high level of efficiency.
Traditional filters are typically made from materials such as fiberglass, synthetic fibers, or activated carbon, and they work by physically trapping particles as the air passes through them. Some common types of traditional air filters include:
HEPA Filters: Effective at capturing small particles like dust, pollen, and pet dander.
Activated Carbon Filters: Primarily used to capture odors, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and some gaseous contaminants.
Electrostatic Filters: Use an electrostatic charge to attract and capture particles.
While traditional filters are excellent at removing particulate pollutants, they have limitations when it comes to dealing with gases, odors, and chemical contaminants.
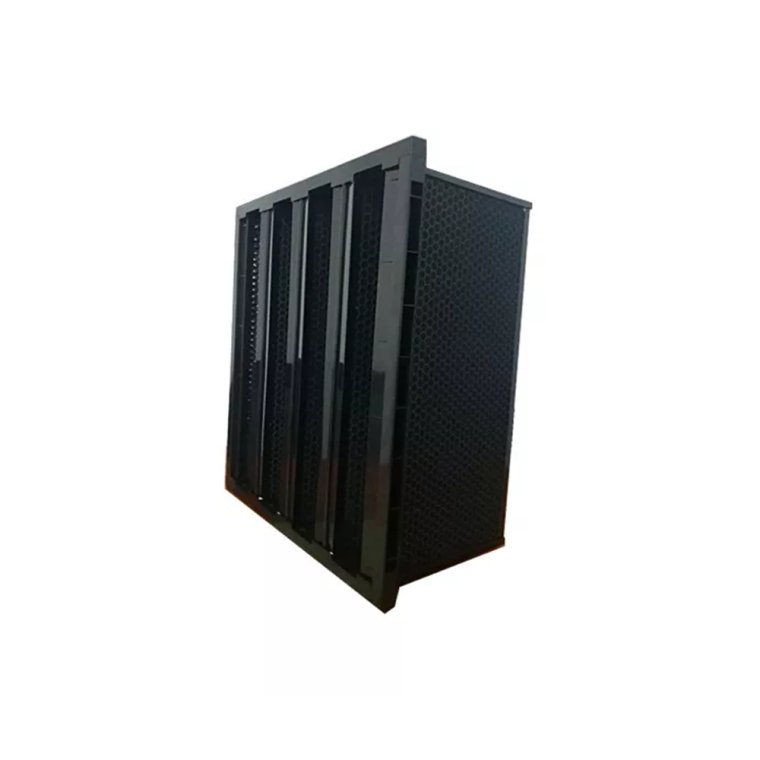

What Are Chemical Air Filters?
Chemical air filters, on the other hand, are specifically designed to target and remove gaseous contaminants and chemical vapors from the air. These filters are often used in environments where chemical exposure is a concern, such as laboratories, industrial facilities, and healthcare settings.
Chemical air filters typically contain activated carbon, zeolite, or other adsorbent materials capable of trapping chemical gases and fumes. Some filters may also be treated with specific substances to enhance their ability to capture certain chemicals. For example, filters can be impregnated with substances that target acidic gases, formaldehyde, or ammonia.
Chemical air filters may not always remove particulate matter effectively, as their primary function is to filter out harmful gases and chemicals. However, in many cases, chemical filters are used in conjunction with traditional filters for comprehensive air purification.
Key Differences Between Chemical Air Filters and Traditional Air Filters
1. Purpose and Functionality
The primary difference between chemical air filters and traditional air filters lies in their functionality:
Traditional Air Filters: Focus on particulate matter, such as dust, allergens, and bacteria. These filters prevent the circulation of airborne particles that can trigger respiratory issues or allergies.
Chemical Air Filters: Designed to filter out gases, vapors, and chemical fumes that can be harmful to human health. These filters are essential in environments exposed to chemicals, such as industrial plants, laboratories, and certain manufacturing processes.
2. Material Composition
The composition of the two types of filters varies significantly:
Traditional Air Filters: Typically made of fiberglass, synthetic fibers, or electrostatic materials. Some may also contain activated carbon to filter out odors and some VOCs, but their primary role is to capture particles.
Chemical Air Filters: These filters are usually made of activated carbon, zeolite, or other adsorbent materials that are highly effective at capturing gases and chemical vapors. Some may contain potassium permanganate or silica gel to further enhance the filtration process.
3. Applications
Both types of filters have distinct applications depending on the contaminants that need to be controlled:
Traditional Air Filters: Best suited for residential, commercial, and office environments where particulate matter is the primary concern. These filters are commonly used in HVAC systems, air purifiers, and in air filtration for homes, schools, and offices.
Chemical Air Filters: Ideal for environments where exposure to harmful chemicals or gases is a concern. These include:
Industrial environments (factories, manufacturing plants)
Laboratories (chemical research, medical labs)
Hospitals (areas with exposure to sterilization chemicals, disinfectants)
Hazardous waste sites and clean rooms.
Agricultural settings, where pesticides or ammonia gas may be present.
4. Performance and Efficiency
Traditional Air Filters: Traditional filters are efficient at capturing larger particles, but their performance may decrease when it comes to smaller particulates or gases. For example, HEPA filters are excellent for particles like dust and pollen but do little to remove gases or odors.
Chemical Air Filters: Chemical filters are optimized to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs), chemical vapors, gases, and odors. However, they are typically not as effective at capturing large particles, which is why they are often used in combination with particulate filters for comprehensive air purification.
5. Lifespan and Maintenance
Traditional Air Filters: Traditional filters typically need to be replaced every 1–3 months, depending on usage and the type of filter. HEPA filters may last longer, but they can become clogged with particles over time, reducing their effectiveness.
Chemical Air Filters: The lifespan of chemical filters can vary widely depending on the chemical load in the environment. Chemical filters must be replaced when they become saturated with the contaminants they are designed to filter out. In industrial settings, this may require more frequent replacements, depending on exposure levels.

Advantages of Chemical Air Filters
Specialized for Chemical Contaminants: Chemical air filters are crucial for environments where harmful gases, vapors, or fumes are present. They offer superior filtration of chemicals compared to traditional filters, protecting workers and occupants from exposure.
Odor Removal: Chemical filters excel at removing unpleasant odors, such as those caused by cleaning products, cooking, smoke, or chemicals.
Comprehensive Air Quality Control: In settings where both particles and gases need to be removed, using chemical filters alongside traditional filters ensures that the air is purified across all types of contaminants.
When to Use Chemical Air Filters
Industrial Facilities: Factories that deal with chemicals, such as paints, solvents, or industrial gases, benefit greatly from the added protection of chemical filters. These filters help prevent the buildup of harmful chemicals in the air, improving both worker safety and product quality.
Healthcare: In hospitals and laboratories, the control of chemical fumes, sterilization gases, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is essential. Chemical filters help maintain a safe and clean environment for patients and medical staff.
Commercial Kitchens: Kitchens often generate strong odors and fumes from cooking, which can be effectively mitigated with the use of chemical air filters. These filters help maintain indoor air quality by removing grease, smoke, and food-related vapors.

Conclusion
The choice between chemical air filters and traditional air filters largely depends on the nature of the contaminants present in your environment. If you need to address airborne particles such as dust, pollen, or pet dander, traditional air filters, especially HEPA filters, are ideal. However, if your environment is exposed to hazardous gases, fumes, or chemical vapors, chemical air filters are the better option.
Accumulating 20 years of experience, AST has developed into an innovative one-source supplier for the air filtration market with filtration products distributed in over 20 countries worldwide.
If you want to Know more about our air filtration products,welcome to contact us.
E-mail:Ivan.shi@airknow.cn