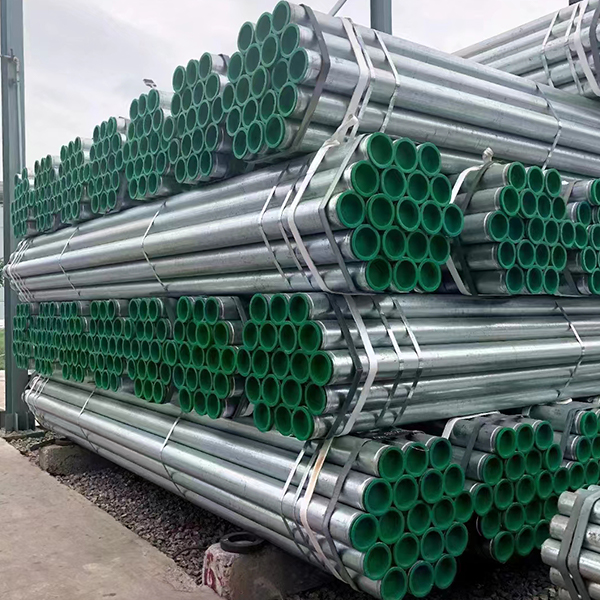
The scaffolding industry operates within a strict framework of safety standards and regulations that govern every aspect of pipe tube manufacturing and usage. These comprehensive guidelines ensure structural integrity and worker safety across construction projects of all scales. International standards such as EN 39 for steel tubes and OSHA regulations in the United States establish minimum requirements for material properties, dimensional tolerances, and load-bearing capacities.
Material specifications form the foundation of scaffolding safety standards. Regulatory bodies mandate specific steel grades that combine adequate strength with necessary ductility. Most standards require minimum yield strengths of 235 MPa or higher, with strict controls on chemical composition to guarantee consistent performance. The wall thickness of scaffolding tubes typically falls between 3.2mm to 4.5mm, carefully calibrated to provide optimal strength-to-weight ratio. These dimensional requirements ensure tubes can withstand design loads while remaining practical for onsite handling and assembly.
Manufacturing processes undergo rigorous scrutiny under current regulations. implement quality control systems that monitor every production stage, from steel coil selection to final inspection. Mandatory testing protocols include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and mechanical property verification. Some certification systems require additional non-destructive testing to identify potential defects that could compromise tube integrity. These measures collectively ensure only compliant products reach construction sites.
Load capacity regulations represent perhaps the most critical safety aspect. Standards prescribe exact calculations for safe working loads based on tube dimensions and material properties. Engineers must consider both vertical dead loads and lateral wind forces when designing scaffolding systems. Modern regulations increasingly emphasize system scaffolding, which offers more predictable performance compared to traditional tube-and-coupler designs. The introduction of digital load calculation tools has made compliance verification more accessible for contractors of all sizes.
Inspection and maintenance requirements complete the safety framework. Regulations typically mandate regular visual inspections by competent personnel, with more thorough examinations at specified intervals. Documentation of inspection results has become increasingly important for liability protection and quality assurance. These ongoing verification processes help identify potential issues before they develop into safety hazards, ensuring scaffolding systems remain reliable throughout their service life.